About Standard Size
Breakdown of standard sizes across various common categories.
1. Standard clothing size chart.
This is one of the most variable categories. Sizes are not standardized between brands or even countries.
US Women's: Typically even numbers (0, 2, 4, 6, ... , 16, 18, etc.)
US Men's: Based on chest/bust measurement (e.g., Size 40 suit).
EU: Uses a number based on a formula (e.g., EUR 36, 38, 40, etc.).
UK: Uses even numbers similar to the US but with different measurements (e.g., UK 8, 10, 12).
2. Standard shoe size chart.
There are three primary sizing systems used around the world: ① US & Canada (North American); ② UK (British); ③ EU (European).
US vs. UK: UK sizes are approximately 1.5 sizes smaller than US men's sizes. (e.g., US 10 = UK 9.5).
US vs. EU: There is no simple formula, but EU sizes are roughly US men's size + 33-34. (e.g., US 10 + 34 = EU 44).
US Men's vs. Women's: There is typically a 1.5 to 2 size difference. (e.g., A men's US 10 is a women's US 11.5).
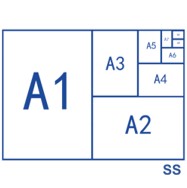
3. Standard paper size chart.
The most recognized global standard is the ISO 216 "A Series", used everywhere except North America.
A3 (297 x 420 mm): Twice the size of A4, often used for presentations and diagrams.
A4 (210 x 297 mm / 8.27" x 11.69"): The international standard for business documents, letters, and printers.
A5 (148 x 210 mm): Half the size of A4, common for notepads and journals.
4. Standard tire size chart.
Companies like U-Haul, FedEx, and Home Depot offer "standard" moving or shipping boxes. Common ones include:
Small: 16" x 12" x 12" - For books, heavy small items.
Medium: 18" x 18" x 16" - The most common, for pots, pans, toys.
Large: 24" x 18" x 24" - For lightweight bulky items like pillows, lampshades.
Tire sizes follow a standardized alphanumeric code on the sidewall. For example: P215/65R15 95H.
5. Standard bed size chart.
Bed sizes follow regional standardization, with North American dimensions differing significantly from European and Asian measurements. Understanding these standards requires examining both historical precedents and practical considerations that shape today's sizing conventions.
North American Standards: The United States and Canada employ an imperial-based system where the queen mattress (60" × 80" or 152 × 203 cm) represents the current bedroom standard. This size emerged in the 1950s as post-war prosperity created demand for larger sleeping spaces, eventually surpassing the full/double bed (54" × 75") in popularity by the 1970s. The twin size (38" × 75") remains the standard for children's rooms and college dormitories, while the twin XL (38" × 80") accommodates taller individuals within institutional settings. The king bed (76" × 80") offers maximum couple space, equivalent to two twin XL mattresses side-by-side, a practical design allowing for independent adjustable foundations. The California king (72" × 84") represents a specialized variation catering specifically to exceptionally tall individuals, sacrificing some width for additional length.
European Standards: Europe follows metric measurements with greater national variation. The standard single bed typically measures 90 × 200 cm, while doubles begin at 140 × 200 cm. The "European king" (160 × 200 cm) corresponds roughly to the North American queen, though Scandinavian countries often extend lengths to 210 cm for taller populations. French bedding sometimes features 160 × 200 cm as "grand lit" while German standards include 180 × 200 cm as "König." Unlike North America's fixed standards, European manufacturers maintain more flexibility within general ranges, resulting in 5-10 cm variations between brands. This requires consumers to verify exact dimensions when purchasing mattresses and linens.
Historical Development and Practical Considerations: Bed sizing evolved from practical constraints. Early 20th-century beds rarely exceeded 54" width due to doorway dimensions and room sizes in urban housing. The standardization of 75" length correlated with average male height in the 1900s, though modern increases to 80" reflect changing anthropometrics. Specialty sizes developed for specific applications: RV mattresses (often 60" × 75") accommodate vehicle constraints, while daybeds frequently utilize twin dimensions for dual-purpose furniture. The bunk bed industry standardized around twin sizes for safety and interchangeability, demonstrating how functionality shapes standardization.