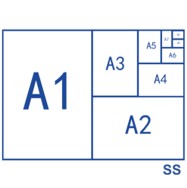
About International Standard Size
About International Standard Classification
The term "International Standard Classification" refers to a system or framework used to categorize and organize information, products, services, or other entities on a global scale to ensure uniformity, comparability, and ease of communication across national borders.
These classifications are developed and maintained by international organizations to facilitate trade, economic analysis, data collection, and regulatory compliance.
What is an International Standard Classification?
It is a standardized coding system that provides a common "language" for:
A. Comparing data across different countries and time periods.
B. Simplifying international trade by harmonizing product descriptions for customs and tariffs.
C. Organizing information in libraries, databases, and statistical agencies.
D. Ensuring safety and interoperability by classifying components, materials, and processes.
Key Examples of Major International Standard Classifications
Here are some of the most widely used and important classifications:
1. ISIC (International Standard Industrial Classification).
Purpose: Classifies economic activities (e.g., industries like agriculture, manufacturing, services).
Maintained by: United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD).
Use: National accounts, economic analysis, comparing economic data between countries.
Example: ISIC Code 6201 refers to "Computer programming activities."
2. HS (Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System).
Purpose: Classifies traded physical goods. It is the foundation for customs tariffs and international trade statistics.
Maintained by: World Customs Organization (WCO).
Use: Customs declarations, trade policies, monitoring controlled goods (e.g., weapons, waste, endangered species).
Example: HS Code 1701.99 refers to "Cane or beet sugar and chemically pure sucrose, in solid form, other."
3. CPC (Central Product Classification).
Purpose: Provides a comprehensive classification of all goods and services. It is often used in conjunction with ISIC.
Maintained by: United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD).
Use: Statistics on production, trade, and consumption.
Example: CPC Code 84322 refers to "Pre-packaged software."
4.ISO Country Codes (e.g., ISO 3166).
Purpose: Standard codes for representing names of countries and their subdivisions.
Maintained by: International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Use: Internet domain names (.us, .de, .jp), international shipping, passports.
Example: US for United States, DE for Germany, JP for Japan.
5.ISO Currency Codes (ISO 4217).
Purpose: Standard three-letter codes to represent currencies.
Maintained by: International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Use: International banking, finance, and business transactions.
Example: USD for US Dollar, EUR for Euro, JPY for Japanese Yen.
6.ICD (International Classification of Diseases).
Purpose: The global standard for diagnosing, managing, and classifying health conditions, diseases, and causes of death.
Maintained by: World Health Organization (WHO).
Use: Epidemiology, health management, clinical purposes, and mortality statistics.
Example: ICD-10 Code I21.4 refers to "Acute subendocardial myocardial infarction."
7.IPC (International Patent Classification).
Purpose: A hierarchical system that categorizes patents and utility models according to the different areas of technology to which they pertain.
Maintained by: World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO).
Use: Searching for patents, assessing the state of the art in technology.
Example: IPC Code A61K 36/00 refers to "Medicinal preparations of undetermined constitution containing material from algae, lichens, fungi, or plants."