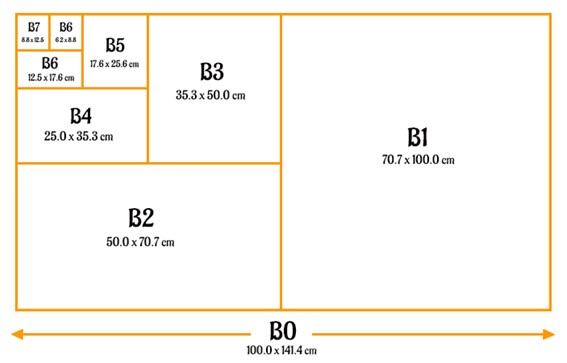
Series B Paper Size
| B Paper Size | Dimensions (inches) | Dimensions (mm) | Area (mm²) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B0 Size | 39.4 × 55.7 | 1000 × 1414 | 1414000 | ||||||
| B1 Size | 27.8 × 39.4 | 707 × 1000 | 707000 | ||||||
| B2 Size | 19.7 × 27.8 | 500 × 707 | 353500 | ||||||
| B3 Size | 13.9 × 19.7 | 353 × 500 | 176500 | ||||||
| B4 Size | 9.8 × 13.9 | 250 × 353 | 88250 | ||||||
| B5 Size | 6.9 × 9.8 | 176 × 250 | 44000 | ||||||
| B6 Size | 4.9 × 6.9 | 125 × 176 | 22000 | ||||||
| B7 Size | 3.5 × 4.9 | 88 × 125 | 11000 | ||||||
| B8 Size | 2.4 × 3.5 | 62 × 88 | 5456 | ||||||
| B9 Size | 1.7 × 2.4 | 44 × 62 | 2728 | ||||||
| B10 Size | 1.2 × 1.7 | 31 × 44 | 1364 | ||||||
| Series B Paper Size Chart Maker : SSize.com | |||||||||
About Series B Paper Size
How are the standard size of B series paper defined?
The B-series paper sizes are defined in relation to the A-series, and their definition is just as elegant.
The Core Definition (ISO 216).
The B-series sizes are the geometric means between corresponding A-series sizes.
A geometric mean between two numbers is the square root of their product. Practically, this means: B(n) is the geometric mean between A(n) and A(n-1).
In simpler terms: A B-size sheet is sized between the A-size with the same number and the next larger A-size.
How It's Calculated.
Let's take B4 as an example:
① A4 is 210 mm × 297 mm.
② A3 is 297 mm × 420 mm.
③ The geometric mean of the side lengths gives B4.
Short side of B4 = √(210 × 297) ≈ √62370 ≈ 250 mm.
Long side of B4 = √(297 × 420) ≈ √124740 ≈ 353 mm.
④ So, B4 is 250 mm × 353 mm.
This relationship holds for all sizes: B1 is between A1 and A0, B5 is between A5 and A4, And so on.
The Starting Point: B0.
Just as A0 has an area of 1 m², B0 is defined to have a side length of 1 meter on its short side.
With the √2 aspect ratio, this gives B0 dimensions of 1000 mm × 1414 mm.
Its area is therefore √2 m² (approximately 1.414 m²).
The halving rule applies identically to the B-series:
B1 is half of B0 (707 mm × 1000 mm).
B2 is half of B1, etc.
Common B-Series Sizes.
Here are some practical examples:
① B2 (500 mm × 707 mm): Used for posters and wall charts.
② B4 (250 mm × 353 mm): Often used for newspapers, large books, and as an intermediate size between A3 and A4 for printers.
③ B5 (176 mm × 250 mm): Very common for books, notepads, and passports in many countries (especially Japan, which uses a slightly different "JIS B" size).
Key Purposes and Advantages of the B-Series.
1. Fills the "Gaps": It provides a wider range of intermediate sizes where the jump between consecutive A-sizes is too large. For example, if A4 is too small and A3 is too big, B4 is a perfect middle ground.
2. Envelopes and Margins: The C-series (used almost exclusively for envelopes) is defined as the geometric mean between the A and B series.
C4 envelope holds an unfolded A4 sheet.
A C4 envelope fits perfectly inside a B4 envelope for extra protection or larger mailings.
This creates a beautifully nested system: A4 → C4 envelope → B4 envelope.
3. Printing and Books: Printers often use B-series sheets for "raw" paper stock. A B1 sheet can be trimmed efficiently to yield multiple A4 pages with room for bleed, crop marks, and binding. The B5 size is a popular book format.